Returning to activity after a sport injury requires careful planning and adherence to medical advice. Engaging in physical activity too soon can worsen the injury or cause new complications. Understanding the steps for diagnosis, treatment, and recovery can help ensure a safe return to sports.
Sports Recovery
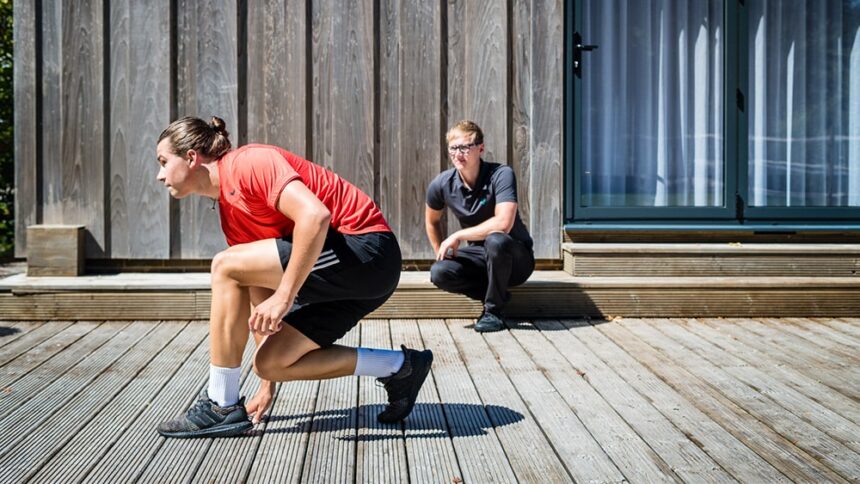
Returning to sports after a sport injury involves a gradual process that prioritizes recovery. Consulting a healthcare provider is the first step, as they can assess the injury and recommend a recovery plan. Starting with light activities that do not strain the injured area is often recommended. For example, individuals recovering from a leg injury may focus on upper-body exercises or low-impact activities.
Physical therapy is often included in recovery plans. It helps rebuild muscle strength and restore range of motion. Gradually increasing the intensity of workouts is important, but any pain or discomfort should be addressed by modifying activities or reducing intensity. Warm-ups, stretching, and cool-down routines can also reduce the risk of re-injury. Following the provider’s recommendations and progressing at a steady pace is important for recovery.
Sport Injury
Diagnosing an injury begins with a review of medical history and a discussion about the circumstances of the injury. Providers ask questions about the cause of the injury, the symptoms, and whether any at-home treatments, such as ice or rest, have been effective. This information helps narrow down potential diagnoses.
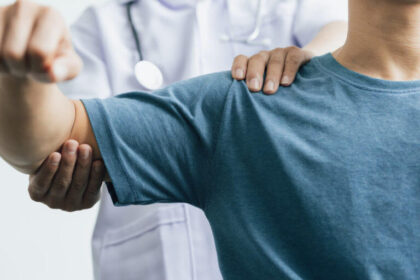
A physical examination is conducted to assess the affected area. Providers may ask patients to perform specific movements to evaluate strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Diagnostic imaging, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, is often used to identify fractures, ligament tears, or soft tissue damage. In some cases, lab tests like blood work or urinalysis are performed to rule out other conditions that could affect recovery.
Sport Treatments
Treatment for injuries depends on the type and severity of the injury, as well as the patient’s age and overall health. Conservative treatments are commonly used and include rest, ice, elevation, and anti-inflammatory medications. These methods help reduce swelling and pain while promoting healing.
Physical therapy is often recommended to restore strength and mobility. Bracing or casting may be used to support and protect the injured area during recovery. For more severe injuries, such as complex fractures or significant ligament damage, surgery may be necessary. In these cases, patients are often referred to orthopedic specialists for further evaluation and treatment.
Preventative measures can reduce the likelihood of future injuries. These include warming up before physical activity, using proper equipment, and following safety guidelines in sports and daily activities.
Meet With A Specialist
Recovering from an injury and returning to sports involves a process that includes accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and a structured recovery plan. An initial evaluation helps identify the extent of the injury and guides decisions about rest, rehabilitation, or additional medical care. Treatment often combines physical therapy, activity modification, and gradual reintroduction of movement to restore strength, flexibility, and coordination. Following medical guidance and allowing adequate time for healing can reduce the risk of setbacks or reinjury. Progression back to sport should occur in stages, with close attention to pain levels, movement quality, and overall function. Because every injury and individual responds differently, recovery timelines vary, and focusing on consistent, measured improvement supports a safer return to physical activity.