The skin serves as a protective barrier against the external environment. Many people will experience some form of skin concern during their lifetime, ranging from temporary and mild to persistent and more severe. Understanding the factors that contribute to skin care is a first step toward managing its appearance and function.
What Are Skin Conditions?
Skin conditions are disorders that affect the skin’s function or appearance. They can manifest as changes in texture, color, or sensation. The development of a skin condition is often multifactorial, involving a combination of internal and external influences. Common contributing factors include:
- Genetics: A predisposition to certain skin conditions can be inherited.
- Immune System Response: An overactive or misdirected immune response can lead to inflammation and skin symptoms.
- Skin Barrier Disruption: A compromised outer skin layer can allow moisture to escape and irritants to enter.
- Allergens and Irritants: Exposure to specific substances can trigger allergic reactions.
- Skincare Practices: The products and routines used to care for the skin can either support or disrupt its health.
What Are the Different Types?
Skin conditions are categorized based on their causes and characteristics. Some conditions can be further divided to specify specific types of conditions. The following are general descriptions of some common types:
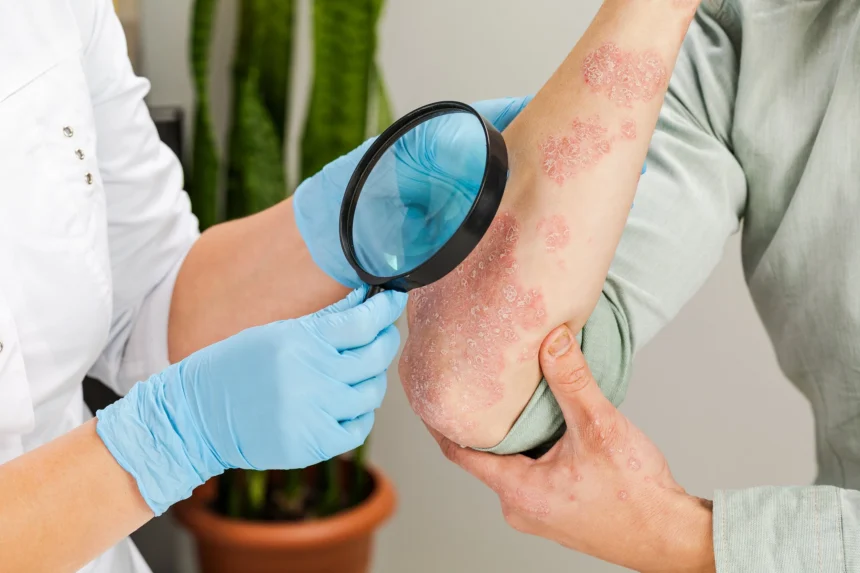
- Dermatitis: This category includes several types of skin inflammation. Atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition often associated with dry, itchy skin. Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to a specific substance.
- Acne: This condition involves the hair follicles and oil glands. It typically appears as pimples, blackheads, or whiteheads and is common on the face, chest, and back.
- Alopecia: This term refers to hair loss from the scalp or other parts of the body. There are various forms of alopecia, which can result in different patterns of hair loss.
- Hives: These are raised, itchy welts on the skin. They often appear suddenly as a reaction to an allergen, medication, or other trigger and are usually temporary.
How Are They Treated?
Managing skin conditions often requires a combination of consistent skin care routines and lifestyle adjustments. Gentle cleansing can help remove impurities without stripping the skin’s natural oils. Consistent use of broad-spectrum sunscreen is a foundational practice for protecting skin from ultraviolet radiation.
Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is also a key management strategy. This may involve tracking diet, product use, and environmental exposures to notice patterns in symptom flare-ups. Implementing stress management techniques may also be beneficial for some individuals. Over-the-counter (OTC) products may be used to address specific concerns. Cleansers or treatments containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid may be used for acne-prone skin.
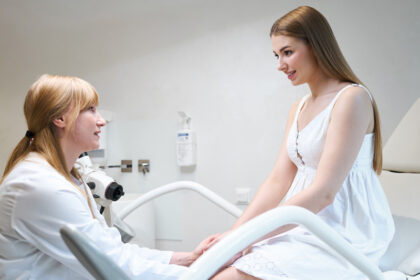
Seek Professional Skin Care
Proper diagnosis is the foundation for effective care. A healthcare professional can distinguish between different conditions that may present with similar symptoms and recommend a course of action based on your unique circumstances. Ongoing monitoring with a professional helps to adjust the management plan as needed and to address any new concerns that may arise. Combining a consistent at-home routine with professional guidance offers a comprehensive approach to managing skin health.