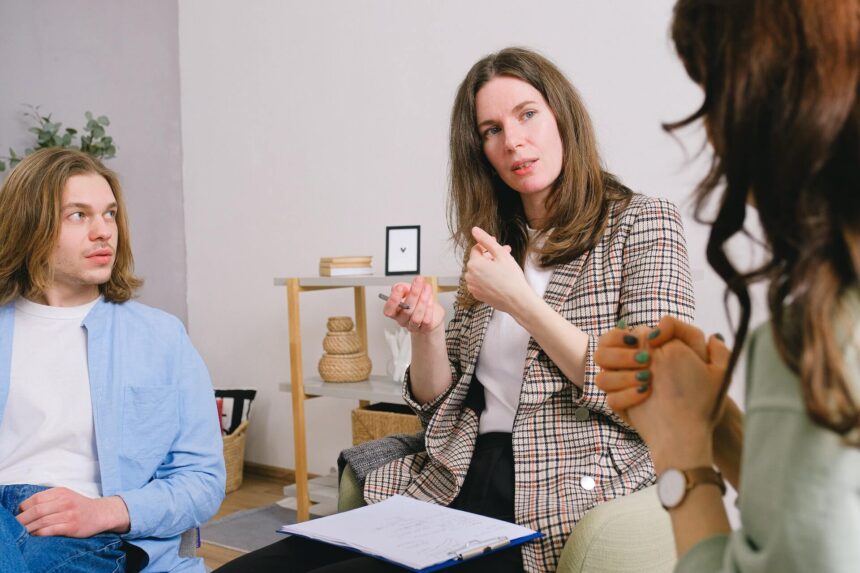
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a condition that affects a person’s ability to focus, control impulses, or manage high activity levels. While medication is often used, behavioral therapies are also very beneficial. They help manage symptoms and improve daily life. These therapies teach new skills, change unhelpful behaviors, and create supportive routines. This helps individuals with ADHD handle challenges at home, school, and work.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a goal-oriented psychotherapy that helps individuals identify and change destructive thinking patterns and behaviors. For those with ADHD, CBT can address secondary symptoms like procrastination and low self-esteem by teaching practical strategies. A therapist works with the individual to reframe negative thoughts, leading to more positive feelings and productive actions.
Developing Coping Mechanisms
CBT helps individuals develop effective coping mechanisms for challenges such as emotional dysregulation. By recognizing triggers for frustration or stress, a person can learn to implement calming techniques before their emotions escalate. This proactive approach allows for better emotional control and stability.
Addressing Time Management
This therapy also tackles difficulties with time management and organization. Individuals learn to break large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps, making projects less overwhelming. This method improves planning skills and boosts productivity in daily life.
Parent Training in Behavior Management
For children with ADHD, parent training in behavior management can be a highly effective therapeutic approach. This training educates parents on strategies to encourage positive behaviors and discourage less helpful ones. Therapists teach parents how to use praise, rewards, and clear consequences to shape their child’s conduct. This approach not only helps manage the child’s ADHD symptoms but also strengthens the parent-child relationship by fostering more positive interactions and reducing conflict within the family.
Organizational Skills Training
Difficulties with organization, planning, and time management are difficult for those experiencing ADHD. Organizational skills training directly targets these executive functioning deficits. This practical, hands-on therapy teaches individuals how to create and maintain systems to manage their daily responsibilities. The goal is to build lasting habits that improve productivity and reduce the stress caused by disorganization. This training often involves learning to use specific tools and techniques, such as:
- Planners and Calendars: Using digital or paper-based systems to track appointments, deadlines, and tasks.
- Checklists: Creating step-by-step lists for multi-part assignments or daily routines.
- Time Management Systems: Implementing methods like timers or specific scheduling blocks to stay focused.
- Physical Organization: Developing systems for organizing papers, workspaces, and personal belongings.
Social Skills Development
Navigating social situations can be challenging for some individuals with ADHD due to symptoms like impulsivity, inattention, and difficulty reading social cues. Social skills development, often conducted in a group setting, helps individuals learn and practice behaviors for interacting positively with others. A therapist guides participants through exercises on topics like active listening, taking turns in conversation, and understanding nonverbal communication.
Explore Therapy Options for ADHD
Behavioral therapies provide helpful tools to manage ADHD symptoms throughout life. They teach coping skills like those in CBT and build practical habits. Parent training helps caregivers with effective techniques. Social skills groups improve how people interact with others. These therapies give individuals and families skills that improve daily life and overall well-being. To find a professional for these therapies, talk to your healthcare provider.