Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health issue that affects millions of people worldwide. If left untreated, it can lead to serious consequences such as tooth loss, chronic infection, and bone damage. In this article, we’ll help you understand what gum disease is, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how to prevent it.
What Is Gum Disease?
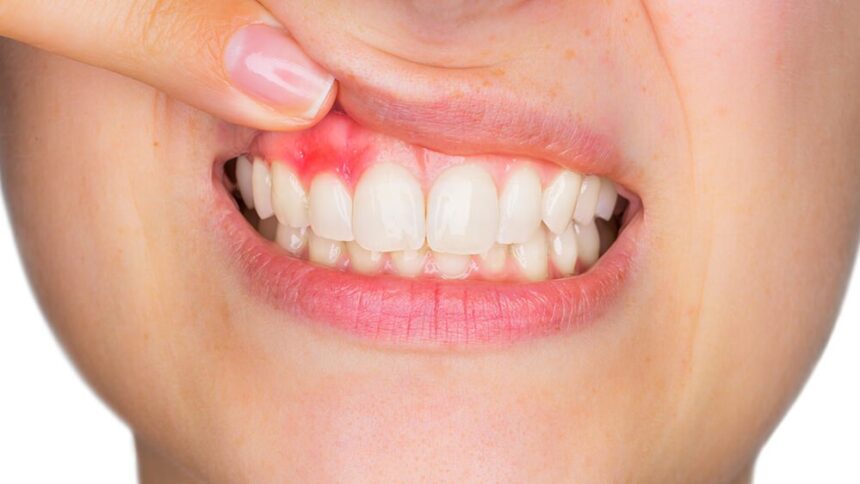
Gum disease refers to inflammation and infection of the tissues that surround and support the teeth. It ranges from mild gum irritation (gingivitis) to severe tissue damage (periodontitis). Early intervention is key to preventing permanent damage.
Stages of Gum Disease
H3: 1. Gingivitis
- The earliest stage
- Caused by plaque buildup on teeth
- Gums become red, swollen, and may bleed easily
- Completely reversible with good oral hygiene
H3: 2. Periodontitis
- Advanced stage of gum disease
- Gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets
- Infection spreads to bone and ligaments
- May lead to tooth loosening or loss
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Identifying symptoms early can prevent progression. Common signs include:
- Swollen or puffy gums
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Pain while chewing
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums
- Sensitive teeth
Note: Some people may experience no pain, making regular dental checkups essential.
Causes of Gum Disease
H3: 1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Improper brushing and flossing allow plaque and tartar to build up, which is the primary cause of gum disease.
H3: 2. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking weakens your immune system and slows healing, making it harder to fight off gum infections.
H3: 3. Hormonal Changes
Pregnancy, menopause, and menstruation can make gums more sensitive, increasing the risk of gingivitis.
H3: 4. Medical Conditions
Diseases like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and cancer can compromise oral health and increase susceptibility to infections.
H3: 5. Genetic Factors
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing gum problems despite good oral care.
H3: 6. Certain Medications
Drugs that reduce saliva flow, such as antihistamines or antidepressants, can increase the risk of gum disease.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
H3: 1. Professional Dental Cleaning
- Removes plaque and tartar above and below the gumline
- Usually sufficient for early-stage gingivitis
H3: 2. Scaling and Root Planing (Deep Cleaning)
- Removes tartar from tooth roots
- Smooths root surfaces to help gums reattach
H3: 3. Antibiotic Therapy
- Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to control infection
H3: 4. Surgical Treatments
For advanced periodontitis:
- Flap Surgery: Lifting gums to clean roots and reduce pockets
- Bone Grafts: Replaces bone destroyed by periodontitis
- Tissue Grafts: Covers exposed roots and prevents further gum loss
Important: Early detection makes treatment simpler and more effective.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Preventive care is the best defense:
| Prevention Tip | Why It Helps |
|---|---|
| Brush twice a day | Removes plaque from tooth surfaces |
| Floss daily | Cleans between teeth and under gumline |
| Use mouthwash | Reduces bacteria and freshens breath |
| Visit dentist every 6 months | Early detection and professional cleaning |
| Quit smoking | Strengthens immune response and healing |
| Eat a balanced diet | Boosts gum and tooth health |
Conclusion
Gum disease is a preventable and treatable condition, but only if caught early and managed properly. Knowing the symptoms and causes helps you stay alert, while regular dental checkups and proper oral care keep your gums strong and healthy. Remember, healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy smile — take care of them before it’s too late.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is gum disease reversible?
Yes, gingivitis (early-stage gum disease) is reversible with proper brushing, flossing, and professional cleanings. However, periodontitis requires more advanced treatment.
2. What is the most common cause of gum disease?
The leading cause is plaque buildup due to poor oral hygiene.
3. Can gum disease lead to tooth loss?
Yes, untreated gum disease can cause tooth loosening and eventual tooth loss due to bone and tissue destruction.
4. How often should I visit the dentist to prevent gum disease?
It’s recommended to visit every 6 months, or more frequently if you have a history of gum problems.
5. Does gum disease hurt?
In its early stages, gum disease is often painless. Pain typically appears in advanced stages when serious damage has already occurred.
6. Can children get gum disease?
Yes, even children can develop gingivitis, especially if they have poor oral hygiene or orthodontic appliances like braces.
7. What’s the best toothpaste for gum disease?
Look for toothpaste containing fluoride, antibacterial agents (like triclosan or stannous fluoride), and one that’s ADA-approved.
8. Can gum disease affect my overall health?
Yes, studies show a link between gum disease and systemic health issues like heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory infections.