As people age, the body’s natural healing processes can slow down, leading to various degenerative conditions. Medical science continues to explore new avenues for addressing these age-related health issues. One area of study is stem cell therapy, a field that focuses on using the body’s own cells to support its natural repair mechanisms. Understanding how this therapy works can provide clarity on its potential applications for age-related diseases.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cell therapy is a form of regenerative medicine that uses special human cells called stem cells. These cells are unique because they can develop into many different cell types, from muscle cells to brain cells. They also serve as an internal repair system, dividing without limit to replenish other cells as long as the person is still alive. This process helps the body heal and maintain itself.
The therapy involves introducing new stem cells into damaged tissue. The goal is for these new cells to promote repair and regeneration in the affected area. Scientists can obtain stem cells from various sources and guide them to become specific cells that may be used to help repair damaged tissues in the body. This approach provides a means to harness the body’s natural restorative functions.
How Does Aging Affect Cells?
Aging is a complex biological process that begins at the cellular level. Over time, cells experience damage or die, while the body’s ability to replace them gradually declines. This cellular deterioration is a significant factor in the development of degenerative diseases and the overall decline in physical function that occurs with age.
One key aspect of aging is the reduced effectiveness of the body’s own stem cells. As stem cells age, their capacity to divide and repair tissues diminishes, leading to slower recovery from injuries. This reduced cellular function impacts tissues and organs, making them less resilient and more prone to damage over time.
The accumulation of cellular damage and the slowing of repair processes are hallmark features of aging. These changes may contribute to the onset of chronic conditions and the gradual loss of function in the body. Supporting cellular health has become a serious focus in tackling age-related diseases, as maintaining healthier cells may improve overall well-being and longevity.
Which Diseases Can Be Treated?
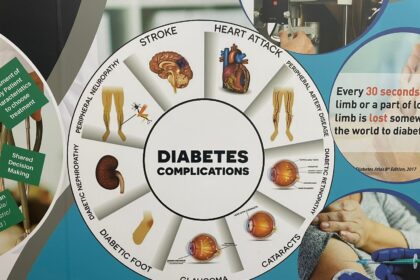
Research into stem cell therapy is exploring its application for various age-related degenerative diseases. The therapy’s objective is to introduce new cells to help repair tissues that have been damaged by disease or injury. This can potentially slow the progression of a condition and improve function.
Researchers are studying this therapy for several conditions, including:
- Osteoarthritis: In this joint disease, the cartilage cushioning the ends of bones wears down over time. Stem cell therapy aims to introduce cells that may help regenerate cartilage and reduce inflammation in the joint.
- Heart Disease: Following a heart attack, heart tissue can become scarred and damaged. The therapy is being investigated as a potential method to repair the damaged muscle and enhance heart function.
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Conditions like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease involve the progressive loss of specific types of nerve cells. Studies are exploring whether stem cells can help replace these lost cells or protect the remaining ones.
- Macular Degeneration: This eye disease causes vision loss through the deterioration of the macula. Research is underway to see if this can repair the damaged retinal cells and restore vision.
Scientists continue to investigate its use in a controlled and systematic way. Each application requires specific protocols to guide the cells and monitor their effects on the body. The field is evolving as more research is completed.
Consult a Specialist
Navigating the complexities of stem cell therapy requires professional guidance. It is helpful to discuss your specific health situation with a qualified medical professional who specializes in this field. They can provide you with accurate information about the current state of treatments and what options may be available to you. A specialist will also explain the processes involved, the types of stem cells used, and what to expect. To learn more about how therapy may apply to your circumstances, schedule a consultation with a healthcare provider.