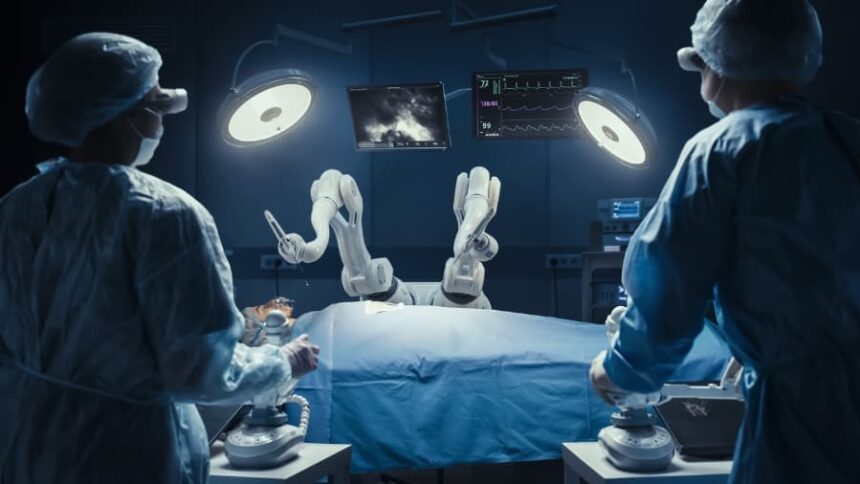
Robotic surgery is a method of performing operations using computer-assisted technology. A surgeon controls robotic arms from a console, translating their hand movements into precise actions with small instruments. This technology allows surgeons to perform complex procedures through very small incisions. Understanding what this type of surgery involves can help you feel more prepared when discussing medical options with your healthcare provider.
Which Procedures Use Robotics?
Many types of procedures can involve robotic assistance. The technology’s precision and minimally invasive nature make it suitable for delicate operations across various medical specialties. Surgeons choose this method based on the specific details of a patient’s condition and the required procedure.
Some common procedures that may use robotic surgery include:
- Prostatectomy: The removal of the prostate gland. The robotic system’s enhanced visualization and dexterity can assist in navigating the complex anatomy of the pelvis.
- Hysterectomy: The surgical removal of the uterus. Robotic assistance can facilitate this procedure through small abdominal incisions.
- Cardiac Surgery: Certain heart procedures, such as mitral valve repair, may be performed using robotic technology to operate within the chest.
- General Surgery: Operations like hernia repair and gallbladder removal can be done with robotic assistance, potentially reducing incision size.
The application of robotic surgery continues to expand as technology advances and more surgeons receive training. Its use is determined by the specific surgical need and the potential to improve patient outcomes.
What Are the Main Benefits?
Robotic-assisted surgery offers several potential benefits stemming from its minimally invasive approach. Because it uses small incisions instead of one large one, the impact on the body may be reduced compared to traditional open surgery. Potential benefits associated with robotic surgery include:
- Smaller Incisions: Robotic instruments require only small openings, which can result in less scarring.
- Reduced Blood Loss: The precision of the robotic arms may lead to less bleeding during the operation.
- Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients undergoing minimally invasive procedures sometimes have a shorter recovery time in the hospital.
These benefits are a direct result of the technology’s design. The surgeon operates with a magnified, 3-D view of the surgical site, which provides a high level of detail. This enhanced vision, combined with the steady motion of the robotic arms, contributes to the procedure’s precision.
What Does Recovery Look Like?
Recovery after robotic surgery varies for each person and depends on the specific operation performed. Because the incisions are small, many people report less pain compared to open surgery. This can make the initial days of recovery more manageable and may reduce the need for pain medication.
Your care team will provide you with specific instructions for your post-operative period. These guidelines will cover wound care, activity levels, and dietary recommendations. Following these directions closely helps support your body’s healing process. You will also have follow-up appointments scheduled to monitor your progress.
Evaluate Robotic Surgery Options
Learning about robotic surgery can help you prepare for discussions with your medical team. This technology represents one of several options available for many procedures, each with its own set of factors. Understanding the basics of how it works, what it is used for, and what recovery may entail provides a foundation for making informed decisions about your care. We encourage you to speak with your doctor to explore all available treatment paths and determine the best approach for your personal health situation.