Internal medicine is a branch of medicine that focuses on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of various diseases. Internists, physicians who practice in this field, manage everything from common illnesses to complex, chronic health issues. Their broad training enables them to solve challenging diagnostic problems and manage severe chronic illnesses. Understanding this field helps you navigate the healthcare system more effectively.
What Is Internal Medicine?
Internal medicine dedicates itself to the comprehensive care of adults. Physicians in this specialty complete a residency program focusing solely on adult medicine after medical school. They differ from family practitioners, who often treat children and perform minor surgeries. Internists equip themselves to handle the broad spectrum of illnesses that affect adults as they age.
These doctors often serve as primary care physicians, but their deep training allows them to manage patients with undefined symptoms and complaints. They coordinate care for patients with multiple overlapping health concerns. Their goal involves treating the whole patient rather than just a single organ system.
Which Subspecialties Exist?
Internal medicine encompasses a wide array of subspecialties, allowing physicians to gain deep expertise in specific organ systems.
Cardiology
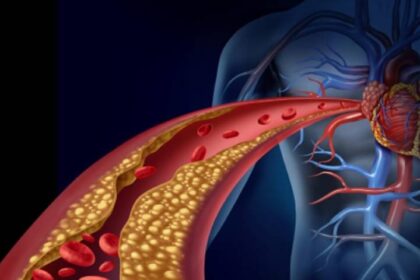
Cardiologists focus on the heart and blood vessels. They diagnose and treat heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and electrophysiology issues. While they manage heart health, they also work to prevent future cardiac events through lifestyle changes and medication.
Endocrinology
Endocrinologists specialize in hormones and the glands that produce them. They treat conditions affecting metabolism, respiration, reproduction, sensory perception, and movement. This specialty often manages diabetes, thyroid diseases, and hormonal imbalances that affect overall well-being.
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterologists handle the digestive system. Their expertise covers the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, rectum, pancreas, gallbladder, bile ducts, and liver. They perform procedures like colonoscopies to screen for cancer and diagnose digestive disorders.
Rheumatology
Rheumatologists treat musculoskeletal disease and systemic autoimmune conditions. These physicians manage arthritis, lupus, gout, and chronic back pain. Their work often involves helping patients maintain mobility and quality of life despite chronic joint issues.
What Conditions Are Treated?
Internists and their subspecialists treat a vast array of conditions, ranging from short-term infections to lifelong chronic diseases. The scope of their practice allows them to address acute illnesses while managing long-term health strategies.
- Hypertension: This condition, often called high blood pressure, requires careful management to prevent heart attacks and strokes. Internists monitor blood pressure levels and prescribe necessary treatments.
- Diabetes: Effective management involves monitoring blood sugar levels, dietary planning, and medication. Specialists help patients avoid complications like nerve damage or vision loss.
- Respiratory Infections: Doctors diagnose and treat infections affecting the lungs and airways, such as pneumonia or bronchitis. Proper treatment speeds recovery and prevents the infection from spreading.
- High Cholesterol: Physicians help patients lower bad cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication. Managing cholesterol reduces the risk of developing heart disease later in life.
Patients benefit from a coordinated approach where the internist oversees the interaction between these various conditions. This oversight prevents treatments for one condition from negatively impacting another.
Consult a Specialist
Navigating health concerns can feel overwhelming, but you do not have to do it alone. An internal medicine specialist serves as a knowledgeable partner in your healthcare. They provide the guidance needed to understand your body and manage your health effectively. Reach out to a local internist today to establish a relationship that supports your long-term well-being.