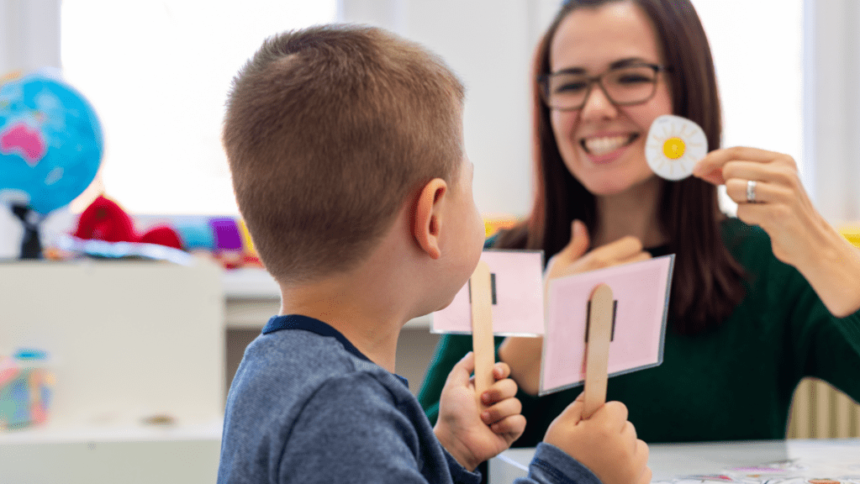
Language skills develop rapidly in early childhood and are crucial for academic and social success. Delays in speech and language can affect learning, emotional development, and peer relationships. Children who struggle to communicate may also experience frustration and behavioral challenges. In pediatrics, early detection of speech issues helps children access support before difficulties interfere with their progress. Addressing concerns early gives children the best chance to build strong communication skills.
What Are Common Signs of a Speech Delay?
While every child develops at their own pace, certain delays can signal a need for intervention. Signs include not babbling by 12 months, not saying single words by 16 months, or not using two-word phrases by age two. Difficulty pronouncing words or being understood by others beyond age three may also be cause for concern. Pediatricians use developmental milestones to help assess whether a child’s speech patterns fall within an expected range or need further evaluation.
Some children may appear to have hearing problems when in fact they’re struggling to process language. Difficulty following directions, answering questions, or responding to their name could indicate an underlying speech or language issue. Children might also repeat phrases or rely on gestures rather than words. In pediatrics, receptive language (understanding) is just as key as expressive language (speaking). A speech therapist can assess how well a child processes and responds to verbal information.
Why Does Limited Vocabulary Matter?
A limited vocabulary for a child’s age may hinder their ability to express thoughts, needs, or feelings. This can impact classroom participation and create challenges with reading and writing later on. If a child uses very few words or relies mostly on gestures or pointing, it may signal a delay in expressive language development. Building vocabulary is a key focus in pediatric speech therapy and often leads to gains in confidence and social engagement.
Difficulty pronouncing certain sounds is common in young children, but persistent trouble with specific consonants or unclear speech may indicate a problem. If a child is often misunderstood by adults outside the family after age three, evaluation might be needed. Speech therapists trained in pediatrics can determine whether sound substitutions, omissions, or stuttering fall within normal development—or suggest a disorder that needs treatment.
Some children struggle not only with speech but also with how they use language socially. Difficulty taking turns in conversation, maintaining eye contact, or understanding humor and sarcasm may signal a social communication disorder. These signs can sometimes be mistaken for shyness or behavioral issues. Speech-language therapy can help children develop appropriate social language and improve peer relationships, especially when challenges are identified early.
When Should You Talk to a Pediatrician?
If you notice ongoing concerns with your child’s speech or language skills, a pediatrician is a helpful first step. They can evaluate development, rule out hearing issues, and provide referrals to specialists if needed. Regular well-child visits often include developmental screenings that can flag concerns early. Pediatricians work closely with speech therapists to create a care plan that supports the child’s long-term progress.
A pediatric speech therapist will observe how a child communicates, both verbally and nonverbally. They may assess vocabulary, sentence structure, understanding, and sound production. Evaluations often feel like play and help identify strengths and areas for growth. Results guide the therapist in creating a tailored intervention plan, with specific goals to help the child build skills in a supportive environment.
Consult Your Pediatrics Provider
Parents and caregivers play a key role in language growth. Reading aloud, naming objects, asking open-ended questions, and modeling clear speech all help reinforce skills. Limiting screen time and increasing face-to-face interaction also boost communication.